Icd 10 Code for Family History of Stroke

Objectives and Skills [edit | edit source]
Part 1: Diagnoses [edit | edit source]
Utilize ICD-x-CM coding guidelines for accurate choice and sequencing of diagnosis codes normally used to describe Diseases of the Circulatory System:
Office ii: Procedures [edit | edit source]
Apply ICD-10-PCS coding guidelines for authentic selection of procedure codes ordinarily used to care for Diseases of the Circulatory System.
Guidelines with Coding Examples [edit | edit source]

Function 1: Diagnoses [edit | edit source]
- Guidelines Introduction Video
- Chapter 9 Guidelines Powerpoint
- Introduction to Chapter 9 Department A Guidelines
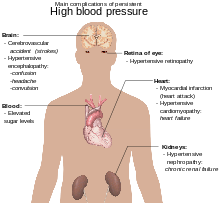
a. Hypertension [edit | edit source]
- Hypertension with Centre Disease.
- Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease
- Hypertensive Center and Chronic Kidney Illness
- Hypertensive Cerebrovascular Disease
 CG ane.C.ix.a.4 Cerebral Aneurysm
CG ane.C.ix.a.4 Cerebral Aneurysm - Hypertensive Retinopathy
- Hypertension, Secondary
- Hypertension, Transient
- Hypertension, Controlled
- Hypertension, Uncontrolled
- Hypertensive Crisis
- Hypertensive Urgency versus Emergency
- Pulmonary Hypertension
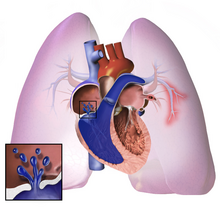 CG 1.C.9.a.11 Pulmonary Hypertension
CG 1.C.9.a.11 Pulmonary Hypertension


b. Atherosclerotic Coronary Avenue Disease and Angina | [edit | edit source]
- Guideline
c. Intraoperative and Postprocedural Cerebrovascular Accident | [edit | edit source]
- Guideline
d. Sequelae of Cerebrovascular Affliction [edit | edit source]
- Category I69, Sequelae of Cerebrovascular illness
- Codes from category I69 with codes from I60-I67
- Codes from category I69 and Personal history of transient ischemic assail (TIA) and cerebral infarction (Z86.73)

e. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) [edit | edit source]
- Type i ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST top myocardial infarction (NSTEMI).
- Acute myocardial infarction, unspecified.
- AMI documented as nontransmural or subendocardial just site provided
- Subsequent astute myocardial infarction.
- Other Types of Myocardial Infarction
Part two: Procedures [edit | edit source]
Apply ICD-10-PCS coding guidelines for authentic selection of procedure codes commonly used to diagnose and treat Diseases of the Circulatory System.
- PCS Root Operation Groups - Ahima
- CMS 2018 PCS Guidelines
Coding Cardiovascular Procedures[i] [ii] [3] [edit | edit source]
- Guidelines Powerpoint | Guidelines Intro | B3.6b | B3.6c | B3.9 | B4.4[4]
- Root Operator Powerpoint[five] | Root Operator Intro | Byapss | Devastation | Map | Dilation | Insertion | Measurement | Replacement | Supplement | Operation[6] [7] [viii] [9] [ten] [xi] [12]
- Case Studies Powerpoint | Coronary Avenue Featherbed Graft (CAGB) x4 | Left Cardiac Catheterization with PTCA | Dual Bedroom Cardiac Pacemaker and Leads
Learning Resource [edit | edit source]
- ACC Hitting Program 2019 Chapter 9 Guidelines Coding Scenerios for each guideline.
- Khan Academy Lessons on Circulatory Organisation Diseases, Symptoms, and Procedures to discover them.
- ICD-x-CM Coding Guidelines: Read Chapter nine guidelines, pages 46-52
- 2019 ICD-10-PCS Coding Guidelines
- 9 Common Heart Surgeries
Procedures Videos [edit | edit source]
-
 Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization | video i | video 2
Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization | video i | video 2 Cardiac Catheterization - Venous Admission Port Catheter
Cardiac Catheterization - Venous Admission Port Catheter - Angiocardiography.
- Intraoperative Fluorescence Vascular Angiography
 Angiography coronary stenosis
Angiography coronary stenosis - Implant of Automatic Cardioverter Defibrillator
- Percutaneous Mitral Valve Repair
- Percutaneous Aortic and Pulmonary Valve Repair
- Percutaneous Balloon Valvuloplasty

- Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
- Transluminal Coronary Atherectomy

- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Video

Coronary Avenue Bypass Graft (CABG)
- Thoracoscopic and Thoracoscopically Assisted Ablation of Eye Tissue (Maze Procedure)
- Totally Implantable and Tunneled Vascular Admission Devices
Activities [edit | edit source]
- HITNOTS.com[thirteen] | Circulatory Coding Quiz | Circulatory Anatomy Quiz | Circulatory Pharmacology Quiz | Circulatory Terminology Quiz |
- Label (Download, print, label and submit) | *Center - meet image on lower right| *Circulatory System - run across epitome on lower right
 |
| Circulatory System to Label
Circulatory System to Label
Lesson Summary [edit | edit source]
Review [edit | edit source]
- Centre and Circulatory Organisation by labeling parts (see Activities)
- Key Diagnosis (see Central Terms)
- Diagnosis Guidelines and Code Scenarios (see Guidelines and Coding Examples)
- Process Guidelines and Code Scenarios (see Guidelines and Coding Examples)
Assessment [edit | edit source]
- Procedures, Diagnosis and Root Operator Assessment Quiz
- HITNOTS.com circulatory coding quizzes
- Quizlet ~ ICD-10-CM Guidelines
Further clarity provided with learning resources. [edit | edit source]
Key Terms [edit | edit source]
Diagnosis [edit | edit source]
- Angina
A status marked by severe pain in the chest, ofttimes as well spreading to the shoulders, arms, and neck, caused past an inadequate blood supply to the heart.
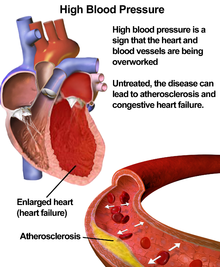
- Atherosclerotic Coronary Avenue Disease
(Also known as: Atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hardening of the arteries) Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a status which affects the arteries that supply the heart with claret. It is normally caused by atherosclerosis which is a buildup of plaque inside the artery walls.
- Cerebrovascular Blow
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is the medical term for a stroke. A stroke is when blood menstruum to a office of your brain is stopped either past a blockage or the rupture of a blood vessel. There are important signs of a stroke that you should be aware of and lookout out for.
- Cerebrovascular Illness
Cerebrovascular affliction includes a variety of medical conditions that bear on the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. ... Narrowed cognitive arteries can lead to ischemic stroke, only continually elevated blood pressure tin also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means your kidneys are damaged and can't filter claret the way they should. The main risk factors for developing kidney disease are diabetes, high claret pressure level, centre disease, and a family history of kidney failure.
- Diastolic Heart Failure
Diastolic middle failure means the lower left sleeping room of the eye (left ventricle) is not able to fill properly with blood during the diastolic phase, reducing the corporeality of blood pumped out to the body.
- Heart Disease
Cardiovascular illness more often than not refers to weather condition that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a middle attack, breast pain (angina) or stroke. Other center conditions, such as those that bear on your heart'due south muscle, valves or rhythm, likewise are considered forms of heart disease.
- Hypertension
High blood pressure level (HBP or hypertension) is when your blood force per unit area, the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your blood vessels, is consistently too high.
- Hypertensive Crunch
A hypertensive crisis is a severe increase in blood pressure that can lead to a stroke. Extremely loftier claret pressure — a top number (systolic pressure) of 180 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) or higher or a lesser number (diastolic force per unit area) of 120 mm Hg or higher — can damage blood vessels.
- Myocardial Infarction
Too known every bit a heart attack which is a sudden and sometimes fatal occurrence of coronary thrombosis, typically resulting in the death of part of a middle muscle.
- Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a life-threatening condition that gets worse over time, but treatments can assistance symptoms. Having pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) means that you take high blood pressure in the arteries that go from your heart to your lungs.
- Retinopathy
Hypertensive retinopathy is retinal vascular impairment caused by hypertension. Signs usually develop tardily in the disease. Funduscopic examination shows arteriolar constriction, arteriovenous nicking, vascular wall changes, flame-shaped hemorrhages, cotton wool-wool spots, yellowish hard exudates, and optic disk edema.
- Systolic Heart Disease
Middle failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), too called systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The center can't pump with plenty forcefulness to push enough claret into apportionment. ... The centre tin't properly fill with claret during the resting catamenia between each crush.
Procedures [edit | edit source]
nine Common Heart Surgeries: From Minimally Invasive to Transplant [14]
- Transmyocardial Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation Revascularization (TMR) – This procedure is usually performed to treat angina when no other treatments work. A small incision is done in the chest to expose the heart musculus, and a high-energy laser is used to make i millimeter wide channels inside the eye. The outer areas of the channels are closed, simply the inner ones remain open to amend claret menstruation. It isn't fully understood how TMR works, but there is show this surgery helps the heart abound tiny new claret vessels, which relieve angina.iii
- Heart Valve Repair or Replacement – In most cases, this is an open up centre operation. The surgeon opens the breast and heart to remove a damaged valve and a prosthetic one is sewn into place. There are some cases where the valve tin can be replaced through a small incision near the breastbone, making the surgery a minimally invasive one.iv
- Heart Transplant – This type of surgery removes the patient's diseased middle and replaces it with a salubrious heart from a deceased donor. This performance is for patients who have stop-stage heart failure, or for people whose heart is very damaged and weak.v
- Arrhythmia Treatment – Although many arrhythmias are harmless, some can be serious and even life threatening. An abnormal heart charge per unit may not pump enough claret to the body, and it may damage the brain and other organs in the body. Some arrhythmias are treated with a pacemaker – a small device that gets placed under the peel of your chest. This device sends electric pulses to help the middle beat at a normal charge per unit. Another manner to care for arrhythmias is an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). This device is besides placed nether the skin of your chest and uses electrical pulses to control arrhythmias. The ICD monitors the centre continuously, if it senses a unsafe arrhythmia, it sends an electric daze to the heart to restore information technology.half dozen
- Aneurysm Repair – An aneurysm is a bulging or an out-pouching portion of a blood vessel. It can occur anywhere in the body, merely it is particularly unsafe if it occurs in the aorta. This may happen when the artery wall weakens, and the blood moving through the artery makes the weak area An aneurysm can burst and cause fatal bleeding inside the body, hence repair surgery is performed prophylactically. The dilated role of the vessel gets removed and replaced with a graft, or constructed material that won't break.7
- Angioplasty – This minimally invasive procedure is used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins. A deflated balloon is attached to a catheter, passed over a guide-wire into the narrow vessel, and then inflated to a stock-still size. Sometimes, a stent is inserted to make certain the vessel remains open, and then the balloon gets deflated and removed.8
- Cardiomyoplasty – This surgical procedure takes healthy muscle from another part of the body, usually the latissimus dorsi from the patient's back; and then it gets wrapped around the centre to provide back up. A special pacemaker is also inserted to make the skeletal musculus contract.9
- Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery – Is performed to exercise some featherbed, middle valve replacement, insert pacemakers, or use some other vein or avenue from the body to employ it equally a graft. As it name suggests, the chest is non cut open, but rather small incisions are fabricated in the right side of the chest, and the surgeon operates betwixt the ribs. The patient experiences less pain and quicker recovery, while it also gives the surgeon a better view of some portions of the heart versus an open-center surgery.
See Too [edit | edit source]
Guidelines [edit | edit source]
- 2019 ICD-x-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting FY 2019(October i, 2018 - September thirty, 2019)
- 2019 ICD-10 PCS
- Wikipedia, ICD-10 Chapter IX: Diseases of the Circulatory Organization
Anatomy/Physiology [edit | edit source]
- MedicalCodingCert: | Role i | Office 2 |
- Circulatory Organisation Animation
Coding Clinic [edit | edit source]
- Ahima Java and Lawmaking. Arteriovenous Graft Revision Coding Clinic. Costless Ahima Webinar for members.
I00–I99 – Diseases of the circulatory arrangement [edit | edit source]
World Wellness Arrangement ICD-10 Training Tool > come across Chapter nine, Circulatory System [edit | edit source]
- Coding: Review of Affiliate (introduction, overview, review, cocky-check exam, exercises and summary)
- Medical Science (anatomy/physiology, diseases and self-cheque examination)
Be mindful when using this tool, that the Us Clinical Modifications are non included. Coding exercises may not display the correct ICD-ten-CM (Clinical Modifications) specific to the United states of america
Chapter IX, ICD-ten [edit | edit source]
Produced past the World Health Organization, it is used in several countries around the world. Some have gone on to develop their own national enhancements, edifice off the international version of the nomenclature.
Chapter 9 of ICD-10 deals with atmospheric condition affecting the circulatory system. Examples of weather captured using codes from Chapter Ix include; Rheumatic fever, Myocardial infarction heart attack, and strokes.
(I00–I02) Acute rheumatic fever [edit | edit source]
- (I00) Rheumatic fever without mention of eye interest
- (I01) Rheumatic fever with center involvement
- (I01.0) Astute rheumatic pericarditis

- (I01.1) Astute rheumatic endocarditis

- (I01.2) Astute rheumatic myocarditis
- Rheumatic fever & middle affliction(I01.8) Other acute rheumatic heart disease
- (I01.9) Astute rheumatic center affliction, unspecified
-
- (I02) Rheumatic chorea
(I05–I09) Chronic (medicine)|Chronic rheumatic heart diseases [edit | edit source]
- (I05) Rheumatic mitral valve diseases
- (I05.0) Mitral stenosis
- (I05.1) Rheumatic mitral insufficiency
- (I05.2) Mitral stenosis with mitral insufficiency|insufficiency
- (I06) Rheumatic aortic valve diseases
- (I06.0) Rheumatic aortic stenosis
- (I06.1) Rheumatic aortic insufficiency
- (I06.ii) Rheumatic aortic stenosis with Aortic insufficiency|insufficiency
- (I07) Rheumatic tricuspid valve diseases
- (I07.0) Tricuspid stenosis
- (I07.1) Tricuspid insufficiency
- (I07.two) Tricuspid stenosis with Tricuspid insufficiency|insufficiency
- (I08) Multiple valve diseases
- (I08.0) Disorders of both mitral and aortic valves
- (I08.one) Disorders of both mitral and tricuspid valves
- (I08.2) Disorders of both aortic and tricuspid valves
- (I08.3) Combined disorders of mitral, aortic and tricuspid valves
- (I09) Other rheumatic centre diseases
- (I09.0) Rheumatic myocarditis
- (I09.1) Rheumatic diseases of endocardium, valve unspecified
- (I09.2) Chronic rheumatic pericarditis
- (I09.9) Rheumatic heart disease, unspecified
(I10–I15) Hypertensive diseases [edit | edit source]
- (I10) Essential (master) hypertension
- Arterial hypertension
- Loftier claret pressure level
- (I11) Hypertensive heart affliction
- (I12) Hypertensive renal affliction
- Hypertensive nephropathy
- (I13) Hypertensive heart affliction and Hypertensive renal illness
- (I15) Secondary hypertension
- (I15.0) Renovascular hypertension
(I20–I25) Ischemic heart diseases [edit | edit source]
- (I20) Angina pectoris

- (I20.0) Unstable angina
- (I20.i) Angina pectoris with documented spasm
- Prinzmetal's angina
- (I20.8) Other forms of angina pectoris
- (I20.nine) Angina pectoris, unspecified
- (I21) Astute myocardial infarction
- (I22) Subsequent myocardial infarction
- (I23) Sure current complications following acute myocardial infarction
- (I23.0) Haemopericardium as current complexity post-obit astute myocardial infarction
- (I23.one) Atrial septal defect as electric current complication following acute myocardial infarction
- (I23.ii) Ventricular septal defect every bit electric current complication following acute myocardial infarction
 Ventricular septal defect
Ventricular septal defect - (I23.3) Rupture of cardiac wall without haemopericardium equally current complexity following astute myocardial infarction
- (I23.4) Rupture of chordae tendineae as current complication post-obit acute myocardial infarction
- (I23.five) Rupture of papillary musculus as current complication following acute myocardial infarction
- (I23.6) Thrombosis of Atrium (heart)|atrium, Correct atrium|auricular bagginess, and Ventricle (middle)|ventricle equally current complications following acute myocardial infarction
- (I23.eight) Other current complications following acute myocardial infarction
- (I24) Other acute ischemic heart diseases

- (I24.0) Coronary thrombosis not resulting in myocardial infarction
- (I24.ane) Dressler'due south syndrome
- (I25) Chronic ischaemic heart disease
- (I25.0) Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, so described
- (I25.one) Atherosclerotic heart illness
- (I25.2) Old myocardial infarction
- (I25.3) Aneurysm of heart

- (I25.4) Coronary artery aneurysm
- (I25.5) Ischaemic cardiomyopathy
- (I25.six) Silent myocardial ischaemia
- (I25.eight) Other forms of chronic ischaemic middle illness
- (I25.9) Chronic ischaemic heart disease, unspecified
(I26–I28) Pulmonary center affliction and diseases of pulmonary apportionment [edit | edit source]
- (I26) Pulmonary embolism
- (I27) Other pulmonary center diseases
- (I27.0) Primary pulmonary hypertension
- (I27.i) Kyphoscoliotic heart disease
- (I27.ii) Other secondary pulmonary hypertension
- (I27.8) Other specified pulmonary centre diseases
- (I27.9) Pulmonary heart disease, unspecified
- (I28) Other diseases of pulmonary vessels
- (I28.0) Arteriovenous fistula of pulmonary vessels

- (I28.i) Aneurysm of pulmonary avenue
- (I28.8) Other specified diseases of pulmonary vessels
- (I28.ix) Affliction of pulmonary vessels, unspecified
-
(I30–I52) Other forms of heart disease [edit | edit source]
Pericardium [edit | edit source]
- (I30) Acute pericarditis
- (I31) Other diseases of pericardium
- (I31.0) Chronic adhesive pericarditis
- (I31.ane) Chronic constrictive pericarditis
- (I31.2) Haemopericardium, non elsewhere classified
- (I31.3) Pericardial effusion (noninflammatory)
- (I31.8) Other specified diseases of pericardium
- (I31.9) Disease of pericardium, unspecified
- Cardiac tamponade
- (I32) Pericarditis in diseases classified elsewhere
Endocardium (including heart valves) [edit | edit source]
- (I33) Astute and subacute endocarditis
- (I34) Nonrheumatic mitral valve disorders
- (I34.0) Mitral (valve) insufficiency
- Mitral regurgitation

-
- (I34.ane) Mitral valve prolapse|Mitral (valve) prolapse
- (I34.2) Nonrheumatic Mitral stenosis|mitral (valve) stenosis
- (I34.0) Mitral (valve) insufficiency
- (I35) Nonrheumatic aortic valve disorders
- (I35.0) Aortic valve stenosis|Aortic (valve) stenosis
- (I35.1) Aortic (valve) insufficiency
- (I35.2) Aortic valve stenosis|Aortic (valve) stenosis with Aortic insufficiency|insufficiency
- (I36) Nonrheumatic tricuspid valve disorders
- (I36.0) Nonrheumatic tricuspid (valve) stenosis
- (I36.ane) Nonrheumatic tricuspid (valve) insufficiency
- (I36.two) Nonrheumatic tricuspid (valve) stenosis with Tricuspid insufficiency|insufficiency
- (I37) Pulmonary valve disorders
- (I37.0) Pulmonary valve stenosis
- (I37.1) Pulmonary valve insufficiency
- (I37.ii) Pulmonary valve stenosis with Pulmonary valve insufficiency|insufficiency
- (I38) Endocarditis, valve unspecified
- (I39) Endocarditis and center valve disorders in diseases classified elsewhere
Myocardium / cardiomyopathy [edit | edit source]
- (I40) Acute myocarditis
- (I41) Myocarditis in diseases classified elsewhere
- (I42) Cardiomyopathy
- (I42.0) Dilated cardiomyopathy
- (I42.1) Obstructive hypertrophy cardiomyopathy
- (I42.ii) Other hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- (I42.3) Endomyocardial (eosinophilic) disease
- Eosinophilic myocarditis
- Endomyocardial (tropical) fibrosis
- Löffler's endocarditis

- (I42.4) Endocardial fibroelastosis
- (I42.five) Other restrictive cardiomyopathy
- (I42.6) Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- (I42.viii) Other cardiomyopathies
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
 Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
-
- (I43) Cardiomyopathy in diseases classified elsewhere
Other [edit | edit source]
- (I50) Middle failure
- (I50.0) Congestive center failure
- Congestive middle failure
- (I50.1) Left ventricular failure
- Cardiac asthma
- (I50.ix) Middle failure, unspecified
- (I50.0) Congestive center failure
- (I51) Complications and ill-defined descriptions of eye affliction
- (I51.0) Cardiac septal defect, acquired
- (I51.1) Rupture of chordae tendineae, non elsewhere classified
- (I51.2) Rupture of papillary muscle, not elsewhere classified
- (I51.3) Intracardiac thrombosis, not elsewhere classified
- (I51.4) Myocarditis, unspecified
- (I51.5) Myocardial degeneration
- (I51.half-dozen) Cardiovascular illness, unspecified
- (I51.vii) Cardiomegaly
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- (I51.8) Other sick-divers heart diseases
- (I51.9) Heart disease, unspecified
- (I52) Other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere
(I60–I69) Cerebrovascular diseases [edit | edit source]
- (I60) Subarachnoid hemorrhage

- (I60.0) Subarachnoid haemorrhage from carotid siphon and bifurcation
- (I60.ane) Subarachnoid bleeding from middle cerebral avenue
- (I60.ii) Subarachnoid haemorrhage from inductive communicating avenue
- (I60.3) Subarachnoid haemorrhage from posterior communicating avenue
- (I60.4) Subarachnoid bleeding from basilar artery
- (I60.5) Subarachnoid haemorrhage from vertebral artery
- (I60.6) Subarachnoid haemorrhage from other intracranial arteries
- (I60.vii) Subarachnoid haemorrhage from intracranial artery, unspecified
- (I61) Intracerebral haemorrhage
 Intracerebral haemorrhage
Intracerebral haemorrhage- (I61.0) Intracerebral haemorrhage in hemisphere, subcortical
- (I61.i) Intracerebral bleeding in hemisphere, cortical
- (I61.2) Intracerebral bleeding in Cerebral hemispheres|hemisphere, unspecified
- (I61.three) Intracerebral haemorrhage in brain stem
- (I61.4) Intracerebral haemorrhage in cerebellum
- (I61.v) Intracerebral haemorrhage, Intraventricular hemorrhage|intraventricular
- (I61.6) Intracerebral haemorrhage, multiple localized
- (I62) Other nontraumatic intracranial haemorrhage
- (I62.0) Subdural haemorrhage (acute)(nontraumatic)
- (I62.1) Nontraumatic extradural bleeding
- Nontraumatic epidural haemorrhage
- (I63) Cerebral infarction

- (I63.0) Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of precerebral arteries
- (I63.i) Cerebral infarction due to embolism of precerebral arteries
- (I63.2) Cognitive infarction due to unspecified Vascular occlusion|occlusion or stenosis of precerebral arteries
- (I63.3) Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of cerebral arteries
- (I63.4) Cerebral infarction due to embolism of cognitive arteries
- (I63.5) Cerebral infarction due to unspecified Vascular occlusion|apoplexy or stenosis of cerebral arteries
- (I63.6) Cerebral infarction due to cerebral venous thrombosis, nonpyogenic
- (I64) Stroke, not specified as hemorrhage or infarction
- (I65) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of precerebral arteries, non resulting in cerebral infarction
- (I65.0) Vascular occlusion|Apoplexy and stenosis of vertebral avenue
- (I65.1) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of basilar artery
- (I65.two) Vascular apoplexy|Occlusion and stenosis of carotid avenue
- (I65.3) Vascular occlusion|Apoplexy and stenosis of multiple and wikt:bilateral|bilateral precerebral arteries
- (I65.8) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of other precerebral avenue
- (I65.9) Vascular apoplexy|Occlusion and stenosis of unspecified precerebral artery
- (I66) Vascular occlusion|Apoplexy and stenosis of cognitive arteries, not resulting in cerebral infarction
- (I66.0) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of center cerebral artery
- (I66.1) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of inductive cerebral artery
- (I66.2) Vascular occlusion|Apoplexy and stenosis of posterior cognitive artery
- (I66.three) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of cerebellar arteries
- (I66.iv) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of multiple and wikt:bilateral|bilateral cerebral arteries
- (I66.v) Vascular apoplexy|Occlusion and stenosis of other cerebral avenue
- (I66.half-dozen) Vascular occlusion|Occlusion and stenosis of unspecified cognitive artery
- (I67) Other cerebrovascular diseases
- (I67.1) Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured

- (I67.ii) Cognitive atherosclerosis
- (I67.3) Progressive Blood vessel|vascular leukoencephalopathy
- Binswanger'due south illness
- (I67.four) Hypertensive encephalopathy
- (I67.five) Moyamoya illness
- (I67.vi) Nonpyogenic thrombosis of intracranial venous system
- (I67.7) Cerebral arteritis, not elsewhere classified
-
- (I68) Cerebrovascular disorders in diseases classified elsewhere
- (I69) Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease
(I70–I79) Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries [edit | edit source]
- (I70) Atherosclerosis
- arteriolosclerosis
- arteriosclerosis
- arteriosclerotic vascular affliction
- atheroma
- (I71) Aortic aneurysm and Aortic dissection|dissection
- (I71.0) Dissection of aorta (whatsoever part)
- (I71.ane) Thoracic aortic aneurysm, ruptured

- (I71.ii) Thoracic aortic aneurysm, without mention of rupture
- (I71.iii) Abdominal aortic aneurysm, ruptured
- (I71.iv) Abdominal aortic aneurysm, without mention of rupture
- (I71.v) Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, ruptured
- (I71.6) Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without mention of rupture
- (I71.8) Aortic aneurysm of unspecified site, ruptured
- (I71.9) Aortic aneurysm of unspecified site, without mention of rupture
- (I72) Other aneurysm
- (I73) Other peripheral vascular diseases
- (I73.0) Raynaud's syndrome

- (I73.1) Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger)
- (I73.8) Other specified peripheral vascular diseases
- Acrocyanosis
- Acroparaesthesia
- Erythrocyanosis
- Erythromelalgia
- (I73.9) Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified
 Peripheral arterial disease
Peripheral arterial disease- Intermittent claudication
- Spasm of artery
-
- (I74) Arterial embolism and thrombosis
- (I77) Other disorders of arteries and arterioles
- (I77.0) Arteriovenous fistula, caused
- (I77.ane) Stricture of artery
- (I77.two) Rupture of artery
- (I77.3) Arterial fibromuscular dysplasia
- (I77.4) Coeliac artery pinch syndrome
- (I77.v) Necrosis of artery
- (I77.half dozen) Arteritis, unspecified
- (I77.8) Other specified disorders of arteries and arterioles
- (I77.9) Disorder of arteries and arterioles, unspecified
- (I78) Diseases of capillaries
- (I78.0) Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
- (I78.1) Naevus, not-neoplastic
- naevus araneus
- spider naevus
- stellar naevus
- (I78.8) Other diseases of capillaries
- (I78.nine) Disease of capillaries, unspecified
- (I79) Disorders of arteries, arterioles and capillaries in diseases classified elsewhere
(I80–I89) Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, non elsewhere classified [edit | edit source]
- (I80) Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
- (I80.0) Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of superficial vessels of lower extremities
- (I80.1) Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of femoral vein
- (I80.ii) Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of other deep vessels of lower extremities
- Deep vein thrombosis NOS
- (I81) Portal vein thrombosis
- (I82) Other venous embolism and venous thrombosis
- (I82.0) Budd-Chiari syndrome
- (I82.1) Thrombophlebitis migrans
- (I82.2) Embolism and thrombosis of vena cava
- (I82.three) Embolism and Renal vein thrombosis|thrombosis of renal vein
- (I82.8) Embolism and thrombosis of other specified veins
- Paget-Schroetter disease
- (I83) Varicose veins of lower extremities
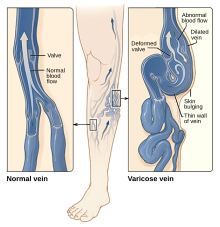
- (I83.0) Varicose veins of lower extremities with ulcer
- Varicose ulcer (lower extremity, any office)
- (I83.one) Varicose veins of lower extremities with inflammation
- (I83.2) Varicose veins of lower extremities with both ulcer and inflammation
- (I83.nine) Varicose veins of lower extremities without ulcer or inflammation
- (I83.0) Varicose veins of lower extremities with ulcer
- (I84) Haemorrhoids
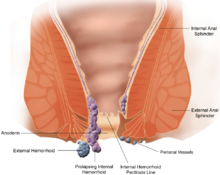
- (I84.6) Rest haemorrhoidal pare tags
- (I85) Oesophageal varices
- (I86) Varicose veins of other sites
- (I86.0) Sublingual varices
- (I86.i) Scrotal varices
- Varicocele
- (I86.2) Pelvic varices
- (I86.iii) Vulval varices
- (I86.4) Gastric varices
- (I86.8) Varicose veins of other specified sites
- (I87) Other disorders of veins
- (I87.0) Postphlebitic syndrome
- (I87.1) Compression of vein
- Superior vena cava syndrome
- (I87.2) Chronic venous insufficiency|Venous insufficiency (chronic)(peripheral)
- (I87.8) Other specified disorders of veins
- (I87.ix) Disorder of vein, unspecified
- (I88) Nonspecific lymphadenitis
- (I89) Other noninfective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
- (I89.0) Lymphoedema, not elsewhere classified
- (I89.1) Lymphangitis
- (I89.8) Other specified noninfective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
- (I89.ix) Noninfective disorder of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, unspecified
(I95–I99) Other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system [edit | edit source]
- (I95) Hypotension
- (I95.0) Idiopathic hypotension
- (I95.one) Orthostatic hypotension
- (I95.2) Hypotension due to drugs
- (I95.viii) Hypotension, other
- (I95.nine) Hypotension, unspecified
- (I97) Postprocedural disorders of circulatory arrangement, not elsewhere classified
- (I97.0) Postcardiotomy syndrome
- (I98) Other disorders of circulatory system in diseases classified elsewhere
- (I99) Other and unspecified disorders of circulatory arrangement
Excludes [edit | edit source]
- Certain weather originating in the perinatal period (P04-P96)
- Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99)
- Complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (O00-O9A)
- Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00-Q99)
- Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases (E00-E88)
- Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes (S00-T88)
- Neoplasms (C00-D49)
- Symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, NEC (R00-R94)
- Systemic connective tissue disorders (M30-M36)
- Transient cognitive ischemic attack an related syndromes (G45.-)
References [edit | edit source]
- ↑ DeVault, Kathryn (2015-ix). "ICD-10-PCS From the Eye: Cardiovascular Procedures". Periodical of AHIMA 86 (nine): 62–64. http://bok.ahima.org/medico?oid=107739.
- ↑ https://world wide web.codebusters.com/?s=bypass+heart+and+not bad+vessels
- ↑ https://journal.ahima.org/2015/02/11/coding-middle-procedures-in-icd-9-cm-and-icd-x-pcs/
- ↑ DeVault, Kathryn (2015-nine). "ICD-ten-PCS From the Heart: Cardiovascular Procedures". Journal of AHIMA 86 (9): 62–64. http://bok.ahima.org/doc?oid=107739#.XIaR7aB7lhF.
- ↑ http://bok.ahima.org/doc?oid=107739#.XIaR7aB7lhF
- ↑ https://world wide web.codebusters.com/coding-tidbits-icd-9icd-10-conversion-scenario-xiii-respond
- ↑ https://www.codebusters.com/coding-tidbits-icd-10-cmpcs-circulatory-organization-reply
- ↑ http://bok.ahima.org/doctor?oid=107739#.XIaR7aB7lhF
- ↑ https://www.miramedgs.com/web/58-the-code-newsletter/mmgs-the-code-spring-2017-issue/678-coronary-avenue-bypass-graft-an-icd-10-pcs-approach
- ↑ https://libmaneducation.com/icd-10-pcs-lets-solve-the-coronary-artery-bifurcation-issue/
- ↑ https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coding/icd10/downloads/gemstechdoc.pdf
- ↑ https://world wide web.codebusters.com/icd-10-pcs-root-operations-part-sixteen-procedures-question-answer
- ↑ "...Circulatory System Quizzes... Athenaeum". Health Information technology Notifications | HITNOTS . Retrieved 2019-02-xvi .
- ↑ Instruments, Sklar. "9 Common Heart Surgeries: From Minimally Invasive to Transplant". inquiry.sklarcorp.com . Retrieved 2019-02-xv .
ICD-x is an international medical nomenclature statistical classification used in health care and related industries.
Source: https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/ICD-10_Coding/Diseases_of_the_Circulatory_System
0 Response to "Icd 10 Code for Family History of Stroke"
Post a Comment